 In the realm of customer feedback and satisfaction metrics, Net Promoter Score (NPS) stands out as a popular and effective tool. However, its implementation isn't without pitfalls.
In the realm of customer feedback and satisfaction metrics, Net Promoter Score (NPS) stands out as a popular and effective tool. However, its implementation isn't without pitfalls.
Understanding the common mistakes when using NPS and how to sidestep them is crucial for harnessing its true potential. Let's delve into the nuances to ensure you make the most out of NPS.
Table of Contents
NPS and Its Relevance

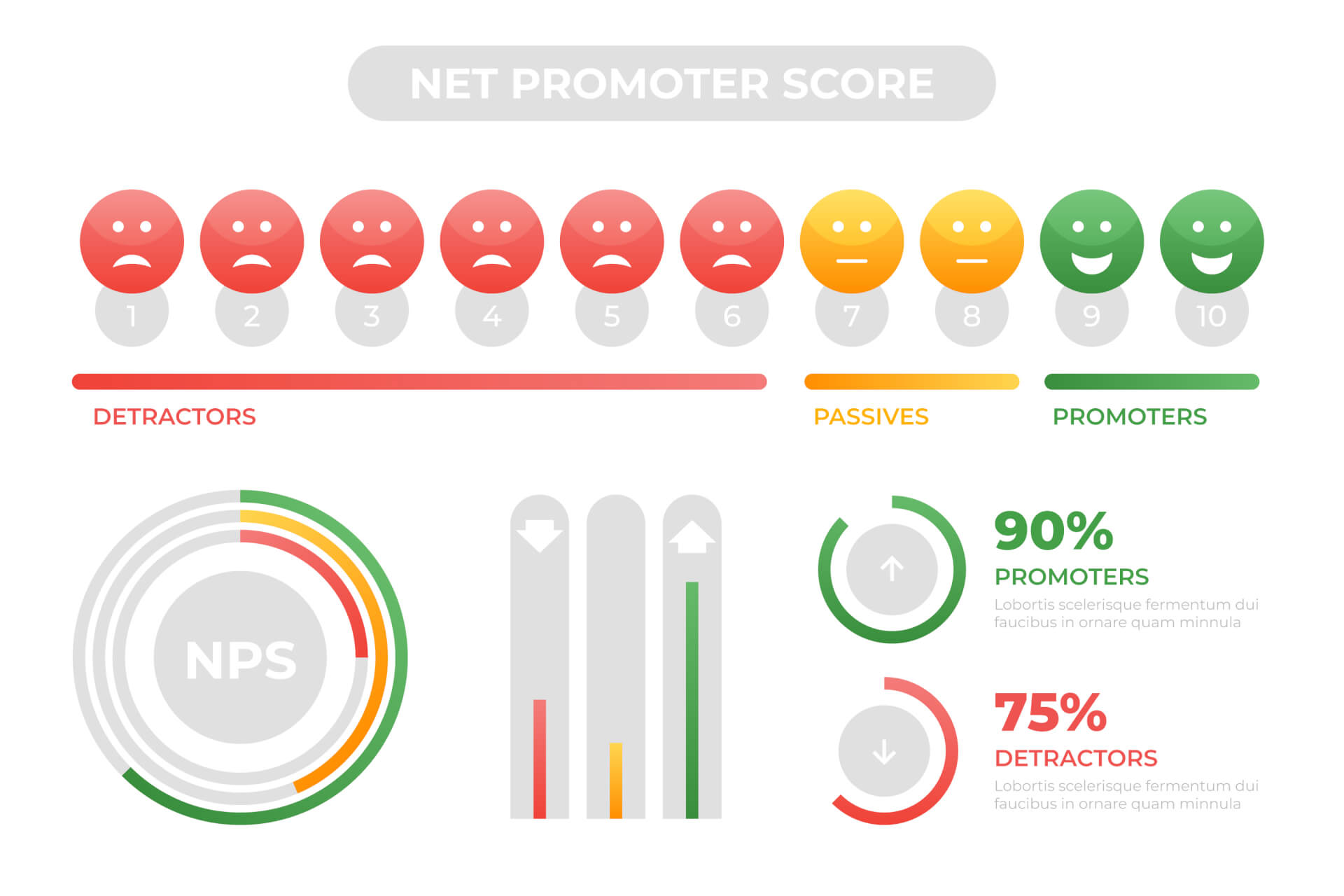
Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a metric used to gauge customer loyalty and satisfaction based on the likelihood of customers to recommend a company's products or services to others.
It's calculated through a simple survey question:
"On a scale of 0-10, how likely are you to recommend us to a friend or colleague?"
Transactional NPS vs. Relationship NPS

- Transactional NPS
Transactional NPS measures customer sentiment after a specific interaction, such as a purchase or customer service call. - Relationship NPS
Relationship NPS assesses overall customer loyalty and satisfaction over a more extended period, providing a broader perspective.
Symptoms and Signs
- Ignoring Detractors
One common mistake is disregarding detractors, those customers who rate your business low. Ignoring their feedback can lead to unresolved issues and potential churn. - Overlooking Promoters
While it's natural to focus on addressing negative feedback, neglecting promoters—customers who rate highly—can mean missed opportunities for advocacy and valuable insights.
Causes and Risk Factors

- Lack of Actionable Insights
Simply collecting NPS scores without analyzing and acting upon the feedback can render the exercise futile, as it fails to drive meaningful improvements. - Misinterpreting Scores
Misunderstanding the significance of NPS scores can lead to misguided strategies. For instance, assuming a high NPS indicates overall satisfaction without considering underlying reasons.
Diagnosis and Tests
- Survey Design Flaws
Inadequate survey design, including ambiguous questions or limited response options, can skew results and compromise the reliability of NPS data. - Timing Issues
Timing is crucial when soliciting NPS feedback. Sending surveys too soon after an interaction may yield inaccurate responses, while delaying them might result in diminished recall.
Treatment Options
Preventive Measures
- Proactive Issue Resolution
Acting swiftly on negative feedback demonstrates commitment to customer satisfaction and can turn detractors into loyal advocates. - Continuous Improvement Initiatives
Implementing a closed-loop feedback process ensures that NPS insights drive tangible improvements across the organization, fostering a customer-centric culture. - Employee Engagement
Engaged employees are more likely to deliver exceptional customer experiences, ultimately impacting NPS scores positively. Investing in training and recognition can bolster employee satisfaction and, in turn, customer satisfaction. - Clear Communication
Transparent communication with customers regarding how their feedback is utilized instills trust and encourages candid responses, enriching the quality of NPS data.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while NPS serves as a valuable tool for measuring customer loyalty and satisfaction, it's imperative to navigate its implementation carefully. By avoiding common pitfalls and adopting best practices, organizations can leverage NPS to drive continuous improvement and foster lasting customer relationships.
 Reading recommendation: If this article helped you and you would like to find out more about the Net Promoter Score, continue reading here: “The Net Promoter Score – Basics and Areas of Application”
Reading recommendation: If this article helped you and you would like to find out more about the Net Promoter Score, continue reading here: “The Net Promoter Score – Basics and Areas of Application”